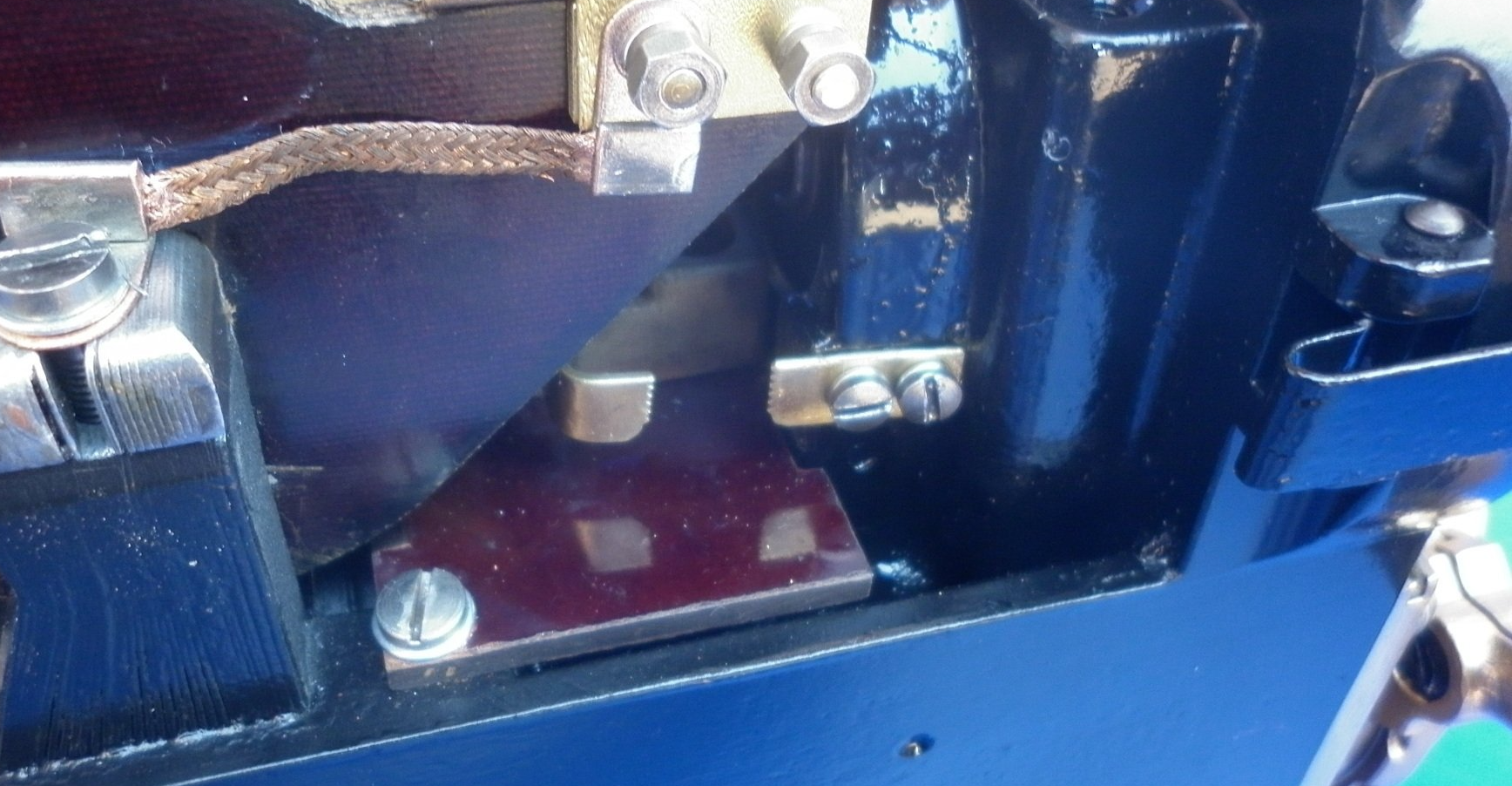
Safety Gaps
Safety gaps come in different forms and are positioned on the magneto in a variety of different places. In all cases, one side of the gap will be attached to the HT circuit, the other will be connected to the magneto body which is earthed. Here are some examples of safety gaps:
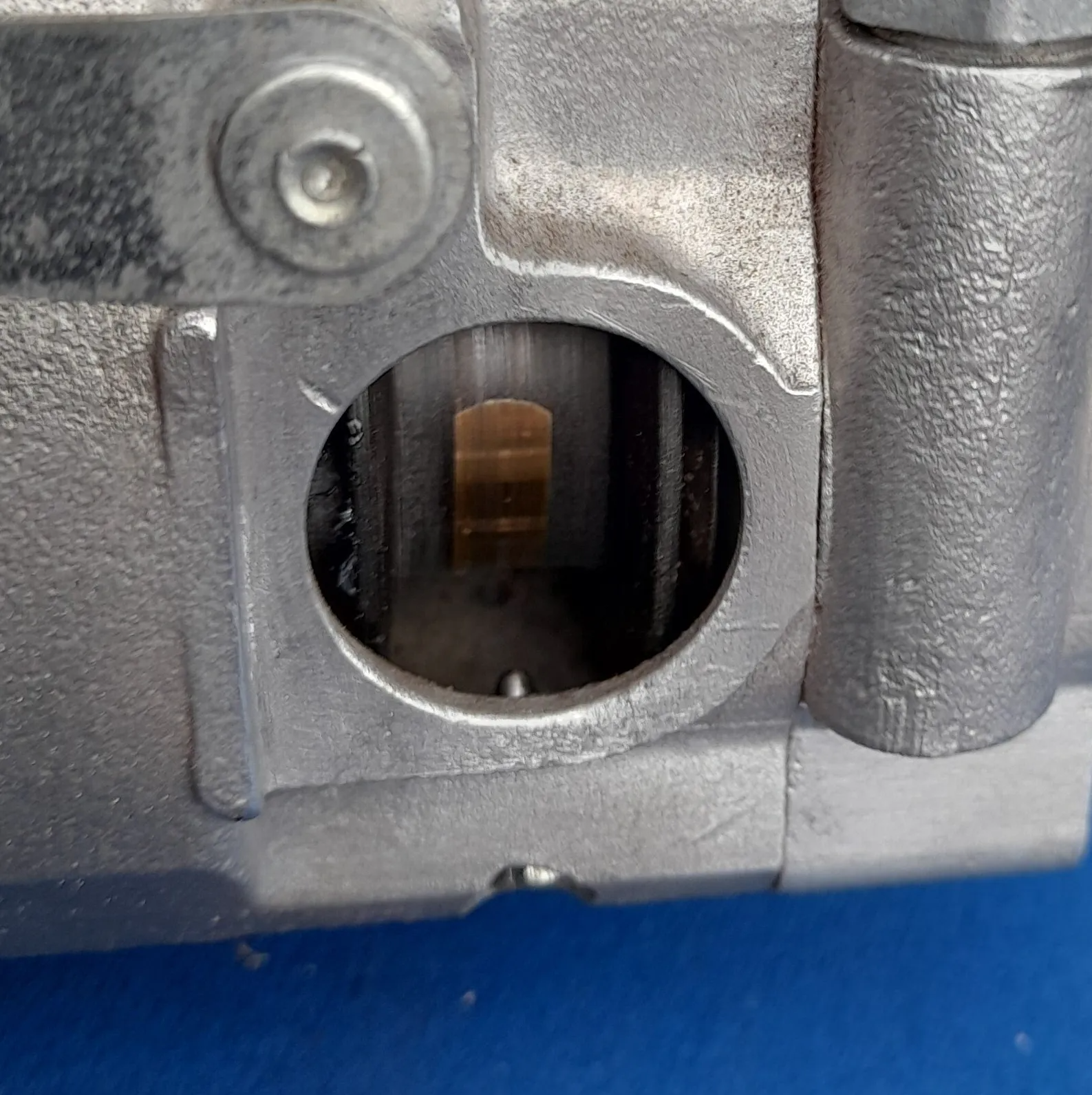
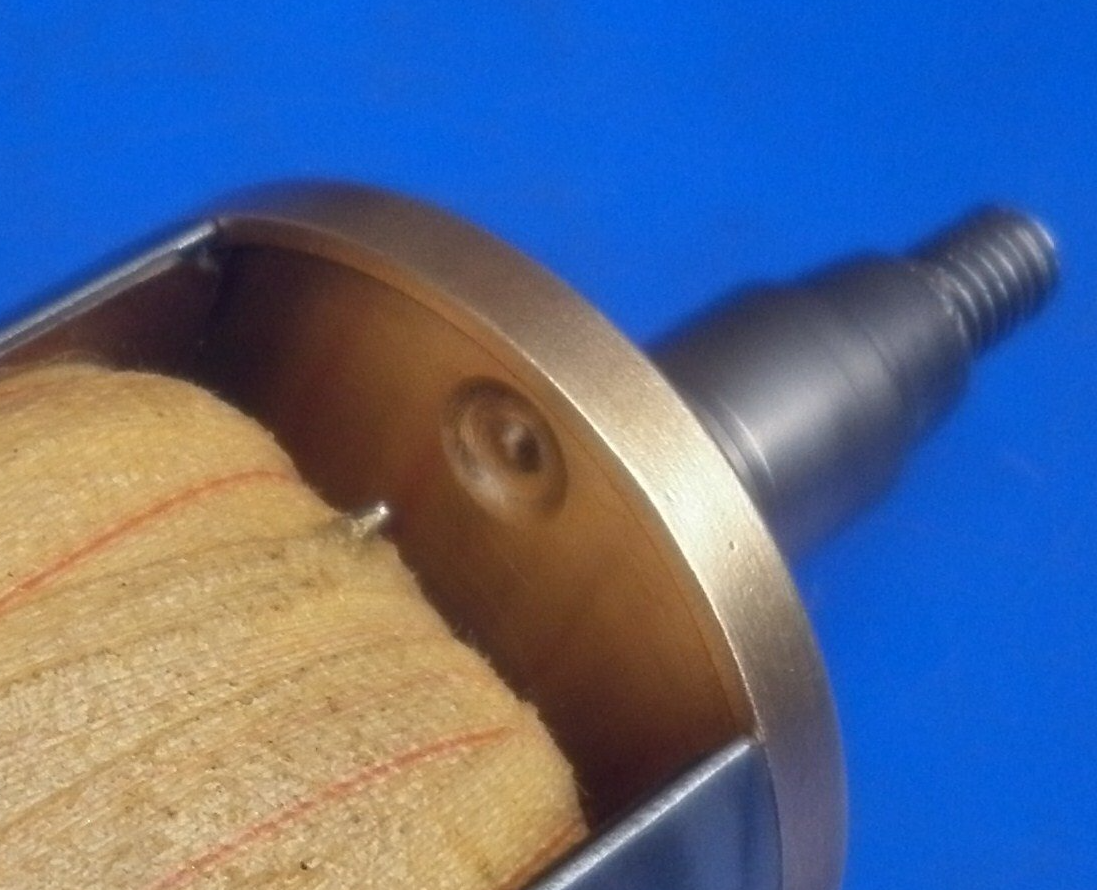

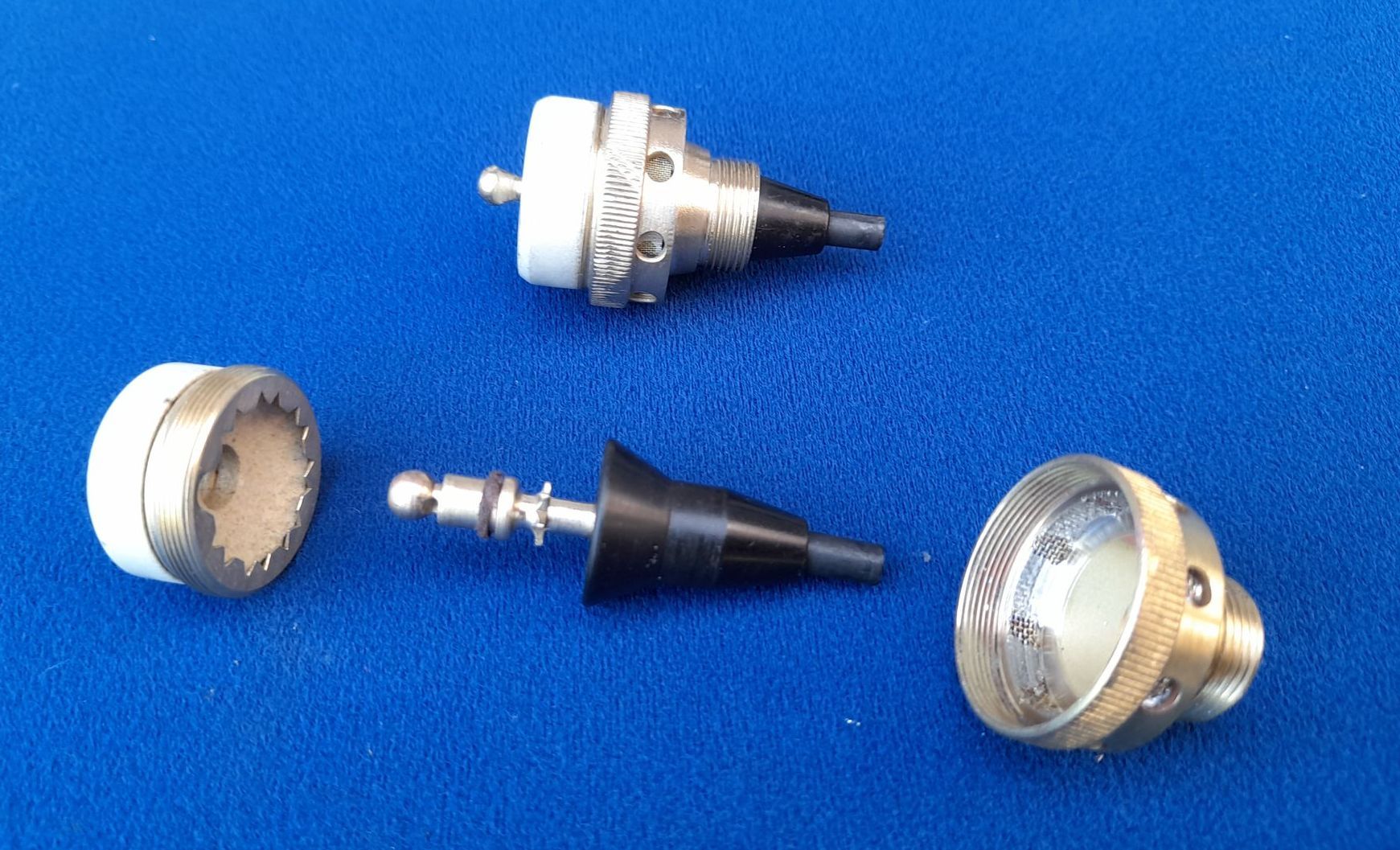
On the twin cylinder Bosch Type D2 magneto, the spark gap is built into the pickups. This picture shows an assembled pickup together with the component parts.
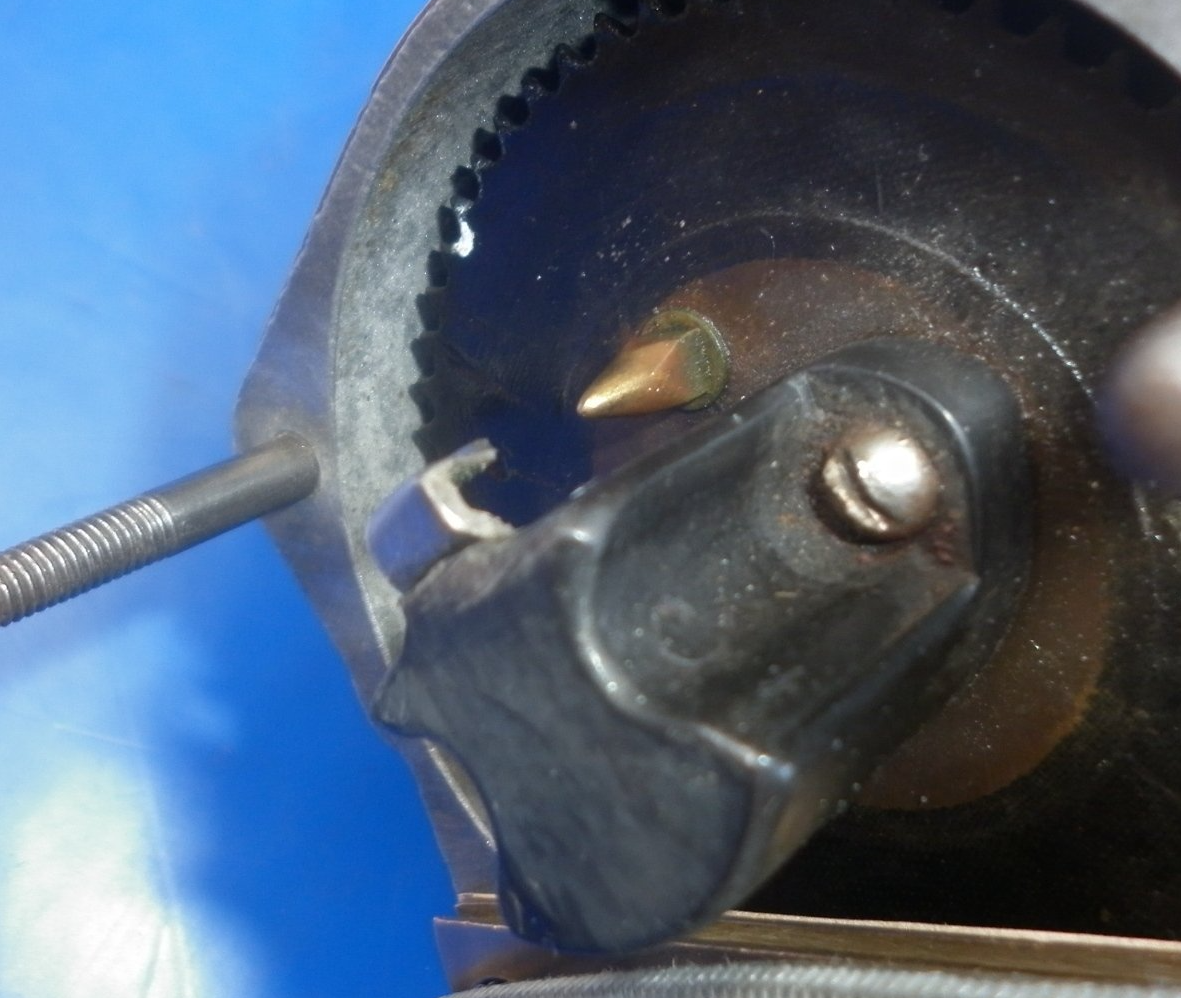

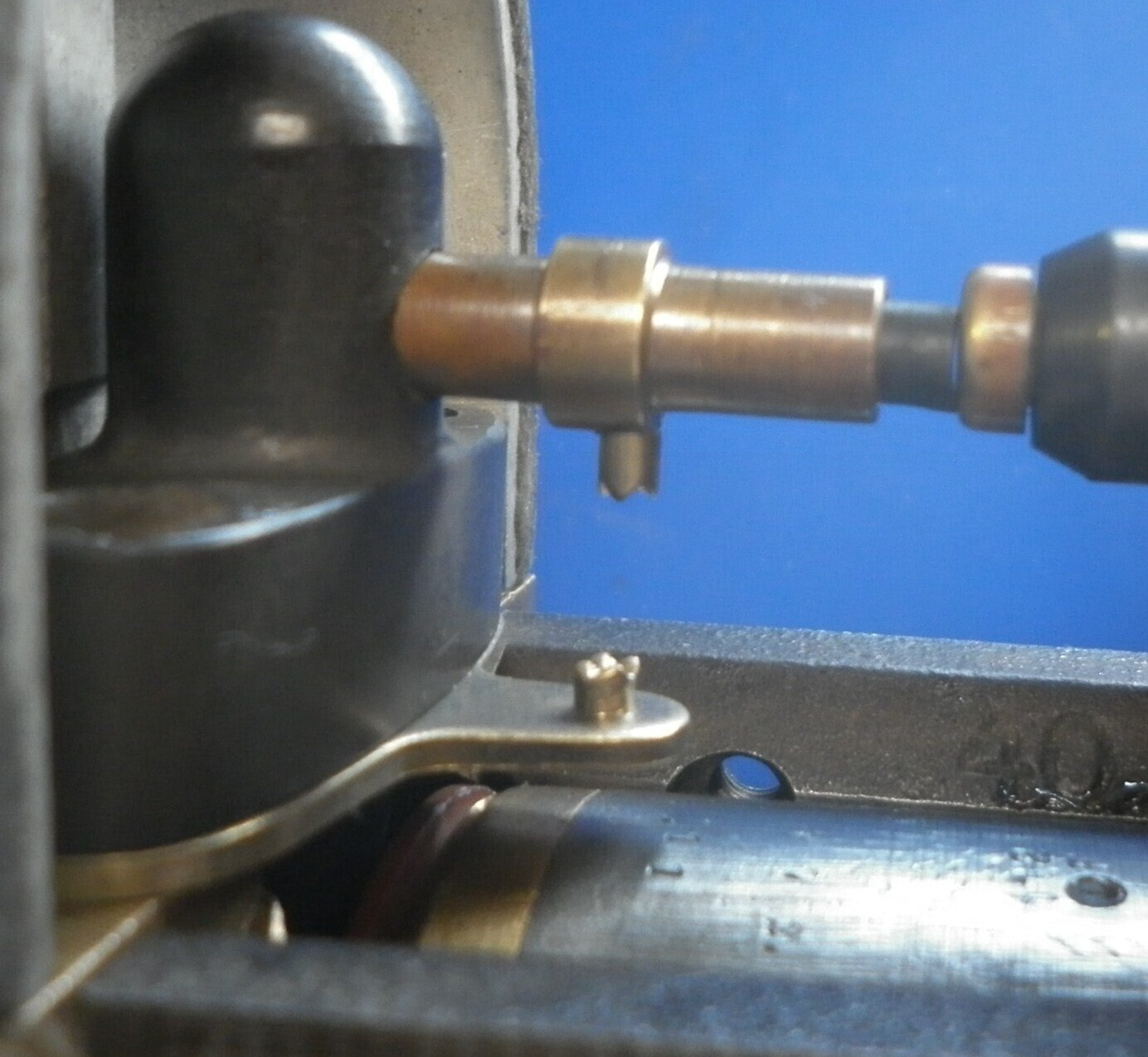

This picture shows the safety gap on a Scintilla GN6 magneto.
The way in which a spark is made to appear across a gap is described on the Voltage at the Spark Plug page. The ionised gas in a gap acts as a conductor thereby allowing current to flow through the gap. For the spark plug gap, the ionised gas is immediately dispersed once the fuel/air mixture is ignited and the power stroke is under way. Under normal operation, no sparks occur at the safety gap but if they do, the ionized air can remain in the gap. This can mean that, when the next spark comes along, the path through the safety gap is an easier route to earth than that provided by the spark plug. This would result in a misfire. Stationary safety gaps would be the most susceptible to this problem. Safety gaps which are always moving such as those mounted on the armature or the rotor arm are better as the air in the gap is continually changing. A misfire caused by a safety gap sparking is not really a major problem in itself. If the safety gap is in use, it is an indication of a problem elsewhere which will need to be investigated and corrected anyway.
The actual size of the safety gap is chosen very carefully. Too small and the spark may occur at the safety gap rather than at the spark plug. Too large and, if the route through the spark plug is not available, the insulation may be over stressed. Period literature for the various magnetos sometimes give a recommended safety gap size. Examples for two of the magnetos shown above are as follows:
The Lucas K1F/K2F/KVF literature indicates a safety gap from the point of the safety screw to the brass segment on the slip ring as 6.5 to 7.5 mm.
The BTH AG4 literature indicates a safety gap of 8 to 8.5mm.

